Summary:
· Stellar revenue growth of 38.9% and operating margins of 28.8% in 2016.
· China's developing consumer economy is a great environment for Alibaba (BABA).
· Short-term target share price projected at $100 in 2017 and $132 in 2018.
· Recommendation: Include BABA shares in the high-risk growth portion of your portfolio.
Main positive factors:
- China's progressing consumer market
- BABA's dominance in the Chinese market
- Stellar revenue growth of 38.9%; Operating margin of 28.8% this year
Main negatives factors and risks:
- Worries over Chinese economy -- slowdown of GDP growth and volatile stock market
- SEC's recent investigation into BABA's accounting
- Unknown valuation of Alibaba's large investment holdings -- more on that later
An Introduction to Alibaba's business
For its giant size, Alibaba is a relatively unknown entity outside of China. Due to its lack of international presence, many are simply not aware of BABA's vast network and domestic dominance even when Alibaba is by far the world's largest online retailer and the 20th largest company in the world by market cap. In 2016, they recorded revenue of $15.3 billion and net income of $10.8 billion.
What people also don't know is that Alibaba is a multi-industry conglomerate. Its core is its e-commerce platforms but it also has significant business and investments in delivery logistics, retail banking, cloud computing, entertainment, and healthcare.
Still the vast majority of revenues, $14.2 billion, come from its e-commerce platforms, the most notable of which are Tmall and Taobao.
- Tmall is a C2C platform much like eBay. Sellers can post items for free and may pay for advertising.
- Taobao is a B2C platform. Here, businesses pay a fee to use the platform and a commission for each transaction. Many international companies use Taobao as their portal to the Chinese market.
These platforms act as a third party by connecting sellers with Chinese consumers. Alibaba never takes on inventory and logistics, instead revenues are earned in the form of commissions, service fees, and advertising. These platforms are popularly used. In China, Alibaba represented 62% of all online sales and according to CNNIC surveys, more than 70% of online shoppers use either Taobao or Tmall as their most frequent online marketplace. The latest quarter reported that there were 423 million active users which was a 16 million increase over the previous year. For comparison, Amazon has 300 million active users.
Internationally, Alibaba's platforms Alibaba.com and AliExpress have a low presence with those sales accounting for 7.5% of total revenue.
Other Businesses Segments
- AliCloud is its cloud computing services. Demand for such services has surged in recent times as businesses look to upgrade systems. Correspondingly, in 2016, AliCloud grew rapidly, earning revenue of $468 million, an increase of 138% from 2015.
- Alibaba owns 47% of Cainaio Logistics, a network of logistics and delivery companies that are in partnership with Alibaba. In 2016, it ran at a loss of $96 million.
- Alibaba owns 37.5% of Ant-Financial. AliPay, China's most popular online payment platform, was spun off from Alibaba in 2011 and renamed Ant-Financial. Since then, it has entered the finance and banking industry, offering personal and saving accounts, credit and loans, and financial investment products. There has been talk of Ant-Financial planning an IPO and if such an event were to occur, BABA would gain a fair amount in equity. With Ant Financial's estimated valuation at $60 billion, BABA would receive a one-time gain of $22.5 billion or $9.4 a share.
- Other notable equity holdings are its purchase of Youku Tudou, a video site like YouTube, for $4.8 billion; 50% of Koubei, a food ordering platform, for nearly $1 billion; and a controlling stake of Lazada, South-Asia's most popular e-commerce platform for $1 billion.
- Other notable enterprising ventures include Alibaba Pictures, media and entertainment; Xia Mi, music; and Ali Health, health care.
Investment Holdings
Because of Alibaba's large equity holdings, gains or losses significantly affect their net income. 73% of their net income in 2016 was from investment-interest income and it was 27% in 2015.

Investment-interest income in 2016 was $8.1 billion, a significant increase from $1.02 billion in 2015. This increase was primarily due to a gain of $3.8 billion from the deconsolidation of Alibaba Pictures and a gain of $2.8 billion from the revaluation of Alibaba Health when they obtained control over it. Note, these investment gains are triggered by certain events that affect accounting and unrealized gains are not recorded until triggered.
Pros and Cons:
With introductions completed, we can move on to analysis. Below is a list of pros and cons that are relevant considerations for Alibaba investors. Lists as such are qualitative analysis -- open to one's own interpretation and personal weighting so consider the pros and cons.
Pros:
- China's economy is a great environment for retail-tech companies like Alibaba. China's demographic is one that is progressing to a consumer economy. Each year, consumers are growing more affluent and both internet and urban infrastructure is growing, allowing easier access to consumers.
- Alibaba is a dominant figure in China. Sellers rely on Alibaba's marketplaces to reach consumers.
- Year over year revenue grew 38.79% in 2016 and 45.14% in 2015, a remarkable growth rate.
- China's domestic market still has room for additional revenue growth. The growth rate for number of active users is still growing quickly - 21% from 2015 to 2016. Additionally, the yearly spending by each of these user increases each year as well - from $25.5 to $28.5 last year.
- As Alibaba does not directly own inventory, warehouses, or trucks, their business model is easily scalable. Operating margins were 28.77% in 2016, very high for retail.
- Unlike many tech companies, Alibaba has positive earnings that produce strong cash flow. As a result, Alibaba's financials are strong.
- Cash from operations are used on acquisitions to expand business into diverse segments and markets.
Cons:
- Possibly unreliable accounting numbers
1. Currently being investigated by the SEC for their sales figures, implications of this are not known yet.
2. SEC may ask BABA to change it accounting methods, namely the way affiliate income is incorporated. For example, of relevance would be Cainiao Logistics, which Alibaba owns a 47% stake in. In 2016, Cainiao recorded a loss of $94 million; Alibaba recorded its percentage of the loss, $46 million, but under incorporation it would post the full amount. This is small in the context of its $10.8 billion net income, however.
- They have little sales outside of China, a trend that is not likely to change as international markets have their own dominant players. E.g. Amazon.
- Earnings are strongly affected by investment income. This makes earnings hard to estimate.
- Many domestic competitors are vying for space in the e-commerce business. Market share among these competitors can change rapidly.
- China's slowdown in economy has been reflected in the previously volatile Chinese stock market. GDP growth has been repeated revised down and its continued descent is forecasted. China's 2016 growth rate was 6.6% and, for reference, USA's 2016 growth rate was 1.8%. 6.6% is a strong growth rate, but the declines still affect consumer sentiment.
- Technically, BABA shares do not equate ownership of Alibaba. Instead shareholders own shares of a Cayman Island variable-interest entity that is entitled to all earnings of Alibaba. This framework is designed to bypass foreign ownership laws in China, a loophole that the Chinese government allows. Such a structure means that if shareholders want to enforce their rights, they will have to do so based on contracts between a Cayman Islands entity and a mainland China one.
Primary Factors Recap:
Pros
- Positive earnings and very strong growth rates.
- Some stability due to its dominance in Chinese markets.
- China's growing consumer class
Cons
- China's slowdown of GDP and market volatility
- Domestic competitors
- SEC investigation into accounting
Overall, BABA shows a lot opportunity but comes with its risks. Again, factors are qualitative, but I believe the opportunity is worth it. Alibaba's business looks strong and their efforts to expand into new markets shows promise. Secondly, China's economy has been rapidly taking steps to evolve. Infrastructure and internet advancements are opening up access to China's more suburban and rural areas while liberalization of financial markets and have propelled growth in Chinese stocks. China can be a rising tide on which Alibaba sails.
Competitors:
It could be argued that Alibaba has a wide moat, based on its dominance, large network, and customer base. However, competition in China is known to be cutthroat with companies rising and falling in popularity extremely quickly. Studies of Chinese consumer behavior have repeatedly found that they show little brand loyalty. Major domestic competitors are JD.com and Vipshop.
JD.com (JD)
- Focuses on domestically manufactured items
- Has a business model like Amazon - owns warehouses and inventory.
- Has almost double the revenue of Alibaba at $27.5 billion but is currently unprofitable with a loss of $1.4 billion in 2015.
- Revenue growth of 57.64% in 2015.
Vipshop (VIPS)
- Focuses on special offers and flash sales.
- Like JD.com, it also holds inventory.
- In revenues, it is half the size of Alibaba, at $6.1 billion
- Low margins of 4% and a net income of $241 million.
- Revenue growth of 71% in 2015.
Alibaba is unique from its domestic competitors in that it operates like eBay - it does not own warehouses or inventory. There are advantages and disadvantages to this set up. The advantage is better margins and scalability, BABA's operating margins were 28.77% in 2016. The disadvantage is lower flexibility in operations and possibly slower delivery times.
Overall, these competitors certainly take up the same market space as Alibaba. However, at this time, growth rates for all the companies are strong. China's consumer market is still expanding which seems to allow all companies to co-exist for now.
Competition internationally is difficult when established companies like Amazon dominate their markets. It is not likely that Alibaba will make much headway into North America, instead it will fight with Amazon over markets in developing markets like South Asia and South America.
Valuation Analysis:
Lastly is an attempt at stock-price valuation through an earnings approach.
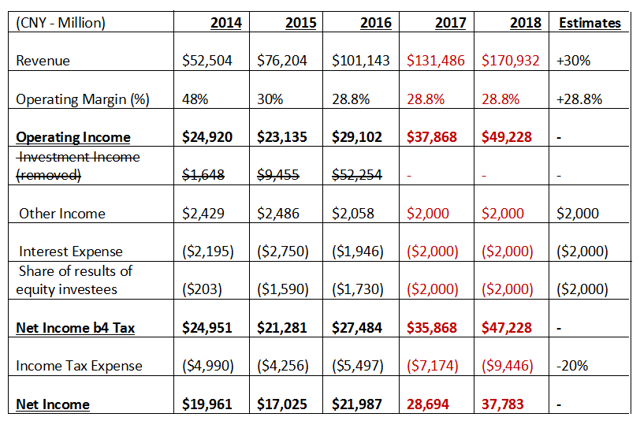
- Based on 2016 figures, a 30% revenue growth rate, 28.8% operating margin, and a 20% income tax expense are assumed.
- Other income, interest expense, and share of results of equity-investees are held at constant for simplicity.
- Investment income is a unique problem. In this valuation, the income from investments has been removed so that the underlying business can be evaluated. There may be investment income in 2017 and 2018, but since it is difficult to get an educated estimate, it has been removed from all years.
Projected Income Statement
Projected EPS/ Share Price
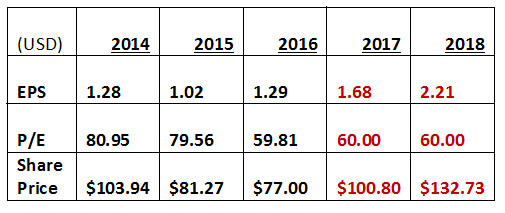
A P/E ratio of 60 is assumed for 2017 and 2018, giving a price valuation of $100 and $132 in 2017 and 2018 respectively.
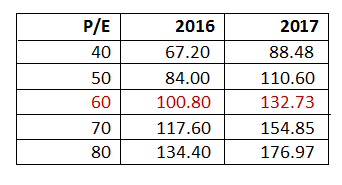
A P/E of 60 would be considered high in other sectors, but for internet-tech stocks, it is more normal. Amazon currently has a P/E of 293, eBay 15, Google 30, Facebook 70, and Vipshop 26, while other companies like Tencent, JD, and Twitter have negative earnings.
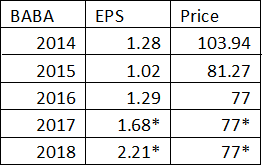
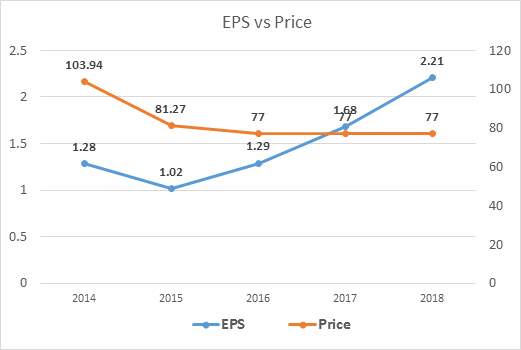
Fundamentally, stock price ought to follow earnings. This line chart is used to visually feel the movement of stock price based on future earnings. The price line, if fundamentals follow, should move upward with the EPS line in the following years.
Conclusion:
Target price - $100 in 2017 and $132 in 2018.
The main positive arguments for BABA are the progressive macro environment in China, its dominance among Chinese users, and its revenue growth of 38.9% and operating margin of 28.8% last year.
The main risks are possible downturns in the Chinese economy, domestic competitors, and SEC's investigation into BABA's accounting.
Overall, strong fundamentals and opportunity. Buy BABA shares as a high-risk growth stock.